While there are many different deer species, most aspects of their vision, including where their eyes are placed on the skull, how they see, what they see, and what they can (and cannot) see are all key to the animal’s survival. As a deer hunter, you need to understand deer vision, but even someone who has a passing interest in deer eyes and why a deer’s vision is unique, you will enjoy this in-depth article.
Understanding what deer see and how they see it, as well as how their vision affects a deer’s behavior, will improve your understanding of deer, and can help hunters enjoy better results.
Let’s begin with the basics about deer eyes and vision.
Eye Size and Placement on the Skull
Deer have eyes that are much larger in proportion to their bodies than we do. With these exceptionally large eyes, deer pupil openings can be enormous.

This is especially true in lower light conditions. When an animal has a large pupil opening, they have better able to gather light in the eye. This improves vision in the dark.
Unlike human eyes, deer eyes are positioned on the sides of the animal’s head. They have a protruding look. Deer eyes are on the sides of the head because it helps deer more quickly detect predators in many circumstances.
Deer’s eyes are placed so that they have a field of vision that wraps approximately 310 degrees around.
As a result of the deer’s eye placement and other elements of its physiology, this animal has a blind spot. To be specific, it’s a 50 degree blind spot that sits between the antlers.
It means that deer have difficulty seeing many areas above them. If you’re a hunter that ever uses tree stands, this is the reason why.
Components of a Deer’s Eye
A deer’s eye has five fundamental components, and they are all found in what is referred to as the ciliary body. The five parts are the lens, cornea, pupil, and retina, as well as the optic nerve head.
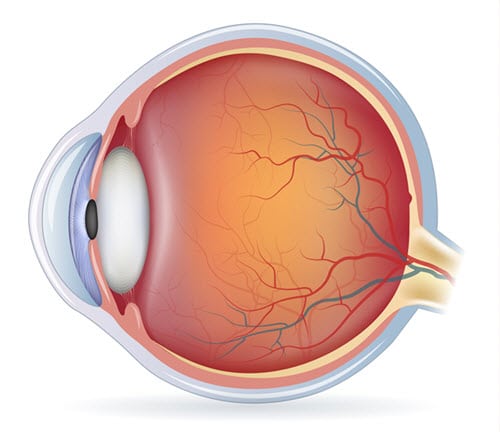
Let’s take a look at each of these components below:
Lens
The lens is found to the rear of the cornea. It is needed to gather the light that comes into the eye, and it directs the light, casting it on the retina.
Cornea
A layer that provides protection to the eye, the cornea protects the lens. In deer, the cornea is completely clear. This is different than the corneas in human eyes, which have UV filters.
The fact that deer corneas don’t have UV filters means that the animals have excellent perception of UV radiance.
Pupil
The pupil has a closing and opening motion that is needed to alter how much light moves into the deer’s eye.
Retina
The retina is found in the back area of the deer’s eye. When light comes in contact with it, there are signals send to the deer’s brain. This is done via the optic nerve.
How Deer See
One of the most important aspects of deer vision is how it is finely tuned to help deer survive. Specifically, it is an essential tool in the process of how deer detect predators and avoid being eaten.

There are several key characteristics of deer eyes which aid in predator detection and deer survival.
Position on Head
The way a deer’s eyes are positioned on its head is part of this. This animal has a 310 degree field of view, with only 50 degrees of blind spot. Compare that to humans, who have three times as big a blind spot.
Internal Eye Structure & Function
The deer’s retina has many more rods in proportion to cones in their retinas. The rods are the components of the eye that act as photoreceptors.
They have intense light sensitivity. However, they’re not great with color. Cones, on the other hand, are responsible for detecting different colors and providing higher resolution in vision.
The shape of the deer’s pupils is also instrumental in how these animal’s see. Out of the three pupil shapes seen in nature (horizontal, round, and vertical), deer have horizontal shaped pupils.
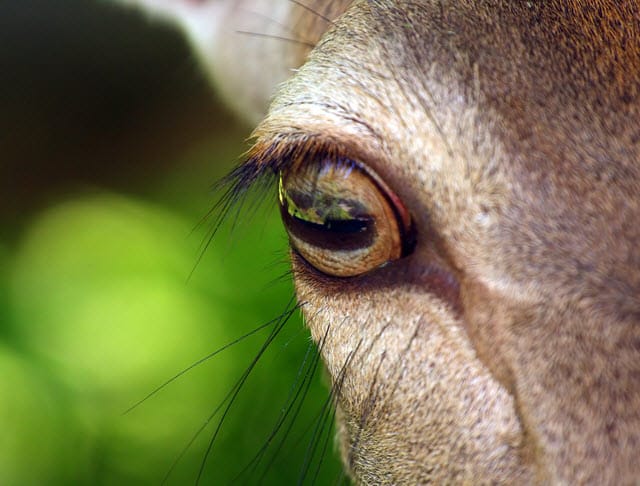

This is common for prey animals. In contrast, predators often feature vertical pupils.
A deer’s horizontal pupils helps deer escape quickly when they detect predators. With their horizontal pupils, deer are better able to see the spaces behind and in front of the threat.
This is why deer won’t end up running in the direction of the predator by accident. Without horizontal pupils, this might be a problem because of the way a deer’s eyes are placed on their skulls.
Motion Sensitivity
The fact that deer have such a high proportion of rods in their retinas is why these animals are so great at detecting even slight motion. The tapetum lucidum is another part of the deer’s eye anatomy and it is key to how its vision works. This is a reflective membrane.

Another animal that has this is the cat. If you’ve ever had a cat, you know how their eyes glow in the dark and how well they see at night. When light comes into the deer’s eyes, it moves over a receptive group of rods and cones in the retina. It then gets reflected back to this area again. This is key to the deer’s outstanding night vision.
The deer’s uncanny talent for detecting movement is down to the proportion of cones to rods that it has in the retina. Compared to the retina of a human eye, the retina of a deer eye doesn’t have as many cones in proportion to rods.
The differences in how and how well deer and humans see can be explained with the way the lens focuses and the different rod and cone proportions. Humans have superior perception of color because we have more cones, while deer have more rods so they have better motion detection but cannot see as many colors.
What Deer See
The world deer see has less distinguishable colors than the one we see. These animals, however, enjoy the benefit of excellent sight in low light conditions.
This is because deer have proportionately many more rod cells than humans. The belief that these animals are “color blind” is incorrect. Instead of being color blind, deer see colors in a different way than you do.
Deer can only be considered color blind when it comes to red and green. The colors that deer see well are green and blue. Blue is a short wavelength color, and green is a middle wavelength color.
Deer aren’t able to tell the difference between orange and red, or green and red. These animals, however, shouldn’t have any trouble telling the difference between blue and red.

Many hunters wonder how deer perceive them. If you wear a bright orange coat, the deer probably perceives that as gray. You may think that this mean you will blend in with the background so much that the animal won’t see you.
However, bright clothing has an ultra-violet effect that deer can perceive. So does any kind of material with a reflective finish. Deer can see this ultra-violet radiance because of how well it sees blue, or short-wavelength, light.
Deer Have Prey Eyes
The position of deer eyes on their head is because they are prey in the food web. They need better peripheral vision in order to quickly perceive potential predators.
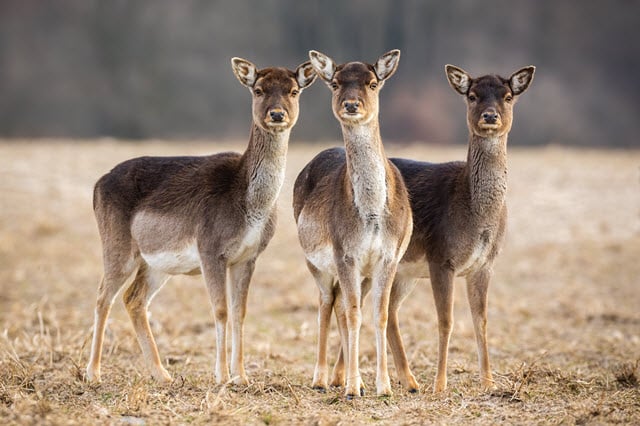

This is different than predators (including humans) that have eyes at the front of their heads. As we’ve discussed elsewhere, deer have a vision band of 300 degrees.
Unfortunately for deer (but fortunately for hunters), there are some disadvantages involved with deer vision. Deer have a low level of visual acuity. In terms we’re used to, deer only have approximately 20/40 vision.
Deer also have poor depth perception for a large amount of their vision, specifically a 60-degree span where there is an overlap in the vision of both eyes.
Deer Night Vision
It’s well known that deer have outstanding night vision that is much better than humans. Experts believe it may be as much as 18 times better. Part of what makes deer night vision so excellent is the shape of the animal’s pupils.
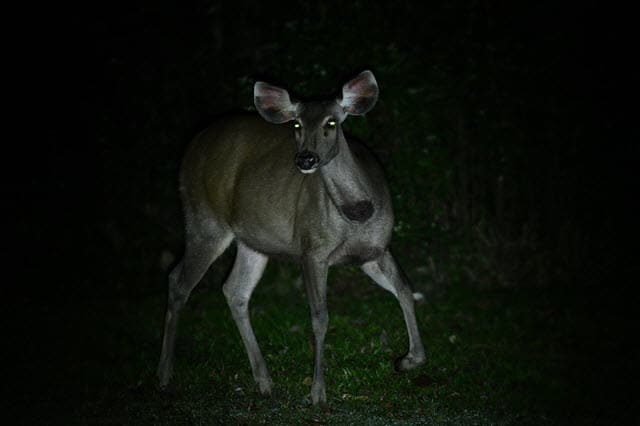

They have a horizontal shape and is much larger than human pupils, which are round. Deer pupil shape and size means that their eyes can bring in nine times the amount of light that human eyes can.
Rods & Cones in Deer Eyes
The features of deer vision means that it works most effectively in lower light. This animal’s retina boasts 20 times the number of rods as they do cones, and rods are key to vision in low light conditions.
Cones are the eye elements that allow for color vision. When conditions are dark or low-light, the rods in a deer’s vision system predominate, and this means that they don’t see colors well in low light.
One of the most significant features that makes deer have such excellent night vision is a layer in the back area of the eye. It’s referred to as the “tapetum lucidum,” and it’s a bit like a mirror. If you’ve ever seen an image of a deer in headlights or headlamps, you’ve seen what the tapetum lucidum does.
It creates the ability for the eyes to more effectively reflect light. When any light enters the deer’s eyes, the light will immediately come into contact with the rods in the retina, which number in the millions.
Once initial contact is done, it comes back to wash over the tapetum lucidum. This creates a bouncing and reflection that will double how much light the deer is able to see and use.
The tapetum lucidum is also able to bring in light that bounces off the ground. Any light that is reflected from the ground will be magnified by the tapetum lucidum, and this creates more contrast that makes it easier for the deer to navigate its surroundings. With this ability, deer can get a better view of details all around them.
How Does the Weather Affect Deer Vision?
As we’ll learn later, rain (and the mist and fog that may come along with it) impedes deer vision. This is why many hunters go out on expeditions in rainy weather. But what about other kinds of weather?

In general, you’re more likely to see deer moving around if the weather is older. In fact, the lower the temperature outdoors, the more likely you are to come across deer during the daytime hours.
Another significant factor is cloud cover. If it’s too cloudy outside, you may have a bit of difficulty seeing deer movement. However, the deer may be more likely to be active, especially if it’s rainy. So whether you see deer will depend on a variety of factors.
Be aware, however, that the clearer the weather, the more likely deer vision will be at its sharpest. If you want to use a deer’s impeded vision to benefit your hunting effort, go with rainy days that will make it harder for them to see.
Should You Hunt Deer in the Rain?
It sounds a bit strange to beginner hunters, but yes, it’s a great idea to hunt deer in the rain. There are a couple of reasons for this, and one of them has to do with the deer’s eyes and vision.
Put simply, rainy weather interferes with how well a deer can see. In other words, the rain will help hide you from the deer.

Deer aren’t like us. While we tend to get a bit grumpy when we get soaked in the rain, deer barely even notice the rain. Except for the heaviest possible rainstorms, you shouldn’t notice rain making deer movement less likely.
In fact, if the rain is bringing in cooler temperatures, you should be much more likely to come across deer.
Many nature enthusiasts have noticed deer seeming to enjoy the rain. In fact, it often cuts down on their skittishness. This combined with how rain obscures their vision makes a rainy day a great day for deer hunting.
This Is because of not only the rain, but also the mist and fog that often comes along with it. Another reason why rain might help is because how it seems to encourage them to be more active and explore their territory, possibly worried about predators.
In addition to impaired vision, reduced hearing and smell is another reason why deer hunting in the rain is a useful idea.
Deer and Blue Spectrum Light
Deer eyes have the greatest sensitivity to blue-spectrum light colors. These are colors that are most prominent during the dawn and dusk. These are the times of day during which deer are most active.

Deer are able to see the difference between blue and red. However, they cannot distinguish between green and red or even orange and red. It seems that deer are able to see tans and light gray more clearly than greens, browns, and dark reds.
Studies indicate that deer are able to see shades of blue as many as 20 times more effectively than humans. Deer are able to discern shades of blue more acutely than humans can perceive reds, even bright reds.
Movement and Deer Vision
In practice, movement is one of the most important elements of deer vision. In other words, that is the element that deer most quickly and strongly perceive.
This makes sense when you consider that deer are prey animals and they must stay alert and aware of predators that may be around them.
A well-known biologist who studied deer vision, Dr. Karl V. Miller, argued that deer have the same level of focus in every circumstance.
They have blurry vision overall, with any movement they perceive punctuating their perception. He explained that how a human sees when he or she squints is how we should imagine deer see. Deer aren’t able to see small details.
How to Hide from a Deer
As a deer hunter, you have to know the best ways to stop yourself being detected and seen by the animals. Do this by fully understanding deer vision and how to trick these animals.
The constraints of deer vision mean they don’t have the best vision in the daylight hours. The fact that they don’t have the same breadth of color vision as we do means that the color you wear isn’t very significant.

The most important factor is that you use an unobtrusive pattern that is similar to the environment. This is why hunters still wear camouflage. Never wear any kind of reflective surface while hunting deer.
As discussed earlier, shiny clothing made of substances such as plastic or vinyl will give off light that deer will quickly see.
As touched on earlier, the fact deer have difficulty seeing clearly when they look up means that hiding in a tree stand is an effective choice.
Deer and UV Light
You should find out whether your clothing creates any UV brightness before you try to hunt deer. Experts have found that deer are able to perceive shorter kinds of wavelengths that are related to UV light.
Find out whether the clothes you wear for hunting are what is referred to as “UV-hot.” To do this, get a blue or UV light and hold it over the clothes.
If you find your clothes glow when you do this, they are creating a UV radiance that deer will be able to perceive. If you want to use these clothes, you should use a special substance that is especially created to remove UV glow.
You should be able to find this kind of product at hunting supply retail stores. Even if you find that your clothes don’t glow when you put them under a blue or UV light, they may take on this unwanted radiance if you wash them in the wrong kinds of laundry detergents.
Only wash your hunting clothes in detergents that are completely free of UV brighteners.
How Deer Vision Impacts these Animals
Deer vision, including what the animals can and cannot see, impacts how they behave and other aspects of their lives. Their vision affects where deer bed down and sleep, as well as where they browse for forage.

The horizontally or oval-shaped pupils of a deer mean that it can see better to the sides, below, and above. With the shape of their pupils, deer are better able to see areas where many of their predators will show up, between the horizon and ground far away and close to them.
One downside of deer pupil shape is that it isn’t as effective for seeing things higher than the horizon. This means that deer have a difficult time seeing any movements anywhere above them.
When deer look up, their pupil gets narrower to prevent too much light coming in during the day. This means that their vision gets weaker. This is one reason why hunters often use tree stands.
What is a Deer Vision Simulator?
Serious deer hunters may look into getting and using a deer vision simulator. This equipment is designed to let humans see in the same way deer do.
Using this kind of equipment can give you a lot more insight into exactly what deer see. When you do this, you’re better able to know how to hide from deer and more effectively hunt them.
There are deer vision simulators available that let you take photos that show what deer see.
One of the most fascinating aspects of deer vision (that you will see with a simulator) is that orange and gray are not distinguishable and look the same. They may appear a shade of gray or yellow to a deer.
Deer Eyes are Unique
As we’ve seen here, deer eyes are different from human eyes. As a result, there are many differences between deer and human vision.

If you plan on hunting deer, you won’t be successful without a good understanding of deer eyes, deer vision, and what they do and don’t see.
When you know about these things, you can figure out ways of hiding from deer and being able to hunt them without being detected too early.
As prey animals, deer have eye and visual system features that fit their needs. Their vision, however, does have its weaknesses.


