RABBITS
Rabbits are beautiful creatures classified as mammals. The animals with backbone and warm blood are called mammals. They have heterodont dentition and different glands. From the scientific class Mammalia, the word mammal originated.
Rabbits are tiny creatures with soft and clear rounded bodies and short ball-like tails. Their ears and legs are long. They have two pairs of upper incisors and one pair of lower incisors which are ever growing and slowly worn down by feeding on vegetation.
Scientific Classification of Rabbits
|
Kingdom |
Animalia |
|
Phylum |
Chordata |
|
Class |
Mammalia |
|
Order |
Lagomorpha |
|
Family |
Leporidae |
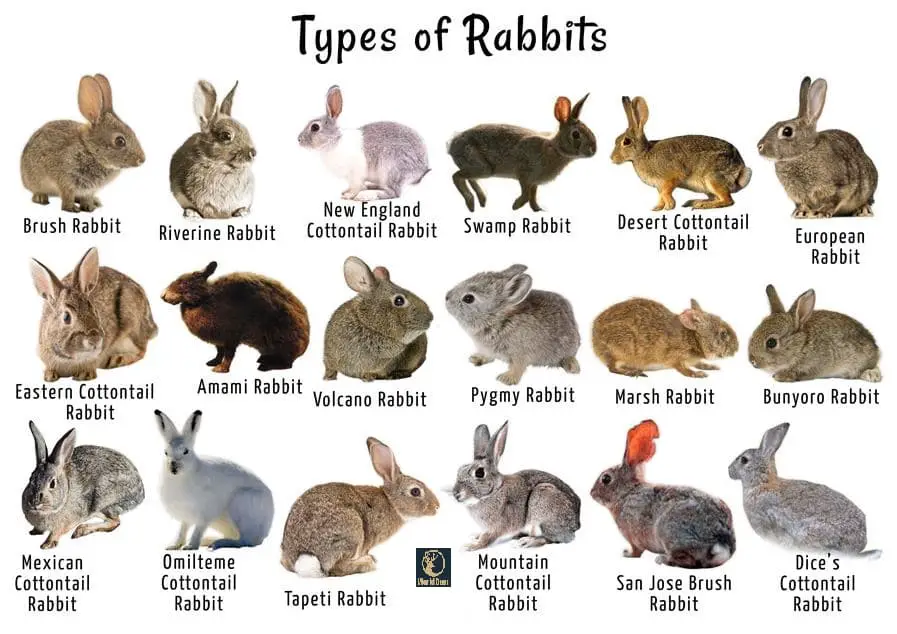
Types of rabbits
Genera: There are about 8 genera under family Leporidae in which rabbits are fully fitted.
- Genus Oryctolagus: European rabbits
- Genus Sylvilagus: 13 species out of which 7 are cottontails.
- Genus Brachylagus: Pygmy rabbit, the world’s smallest rabbit
- Genus Nesolagus: Striped rabbits
- Genus Bonulagus: Bushman rabbit
- Genus Romerolagus: Volcano rabbit
- Genus Pentalagus: Amami rabbit, found in Japan
- Genus Poelagus: Central African rabbit
Exception: Jackrabbits and hares are the mammals that fall under the Genus Lepus
Breeds: There are about 191 breeds of rabbits in 70 countries of the world out of which 50 are recognized as unique by the American Rabbit Breed Association (ARBA).

Description
- Weight: 1.5 to 2.5 kg ( 6-20 lbs)
- Length: 35 to 45 cm ( 1.5- 2.5 ft )
- Dentition: 2 pairs of upper & 1 pair of lower incisor
- Ears: 2 to 26 inches long
- Eyes: moving at 360 degrees
- Speed: Up to 80 km per hour
- Coloration: They usually range in shades of red, brown, and gray. It also shades whitish, buff gray, and a little black. They are brownish on the upper side and have a white shade down the body. Males are usually larger than females.

Rabbit Height
Rabbit Weight

Rabbit Speed
Distribution
There are about 29 species of these long-eared mammals belonging to the Leporidae family except Hares. A well-known rabbit species, European rabbits ( Oryctolagus cuniculus) introduced worldwide. Almost all breeds of domestic rabbits belong to the cuniculus. Geographically, the range of rabbits is from eastern to western hemisphere. They are present in the whole world except Antarctica but are native to the Italian peninsula.
Habitat
Rabbits are animals that dwell in the ground to make burrows for living and to ensure safety from predators. These burrows have more than one entrance for locomotion. Their habitat preference is the area of trees and shrubs where they live in burrows such as
- Forests
- Grasslands
- Wetlands
- Deserts
- Tundra
- Meadows
The same burrows can go to 10 feet in depth. European rabbits developed an extensive burrow system known as warren where almost 20 rabbits live together. Hispid hares and cottontails are non-burrowing rabbits that make surface nests called forms protective under dense cover.

Nutrition and Digestion
Herbivores are animals that feed mostly on vegetation but sometimes eat invertebrates during feeding. According to the definition, rabbits are called herbivores.
They preferred to eat grass, herbs, soft vegetables, and fruits such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, seeds, dewberry, barks, and twigs. The whole food contains a large amount of cellulose which is hard to digest for herbivores.
To overcome this problem, rabbits pass two types of feces, hard droppings and soft black pellets. The soft feces forms at the large cecum, a specialized digestive tract present at the junction between the small and large intestines. Cecum acts as a fermentation pouch where microorganisms help in digestion.
Rabbits are natural recyclers. They eat up their soft feces (coprophagy) which contains five times more vitamins than hard feces. It is redigested in the special part of the stomach. They utilize the nutrients by double digestion to derive the maximum nutrition from food, which they may have missed during former digestion.
Lifespan
In the wild, the maximum lifespan of a rabbit is about 3 years due to the predators. If escaped from predators such as foxes, wolves, stoats and cats, they averagely live up to 8 to 9 years. Lifespan may be extended to 12 years under the captivity of high nutrition and quality wellness.
Sleeping hours
Rabbits take a long nap as they sleep 8 to 10 hours a day. Night shift is apart. As rabbits are crepuscular active at dawn, dusk, and night for food and exercise, that’s why they sleep during the day.
Natural predators
Every creature has some beasts against him that may harm or engulf it to reduce their appetite. This is not bad as it is a natural food cycle to balance each one. Reported natural predators of rabbits are lynx, foxes, cats, stoats and birds of prey such as golden eagle, eagle owl etc.

Rabbits and Foxes
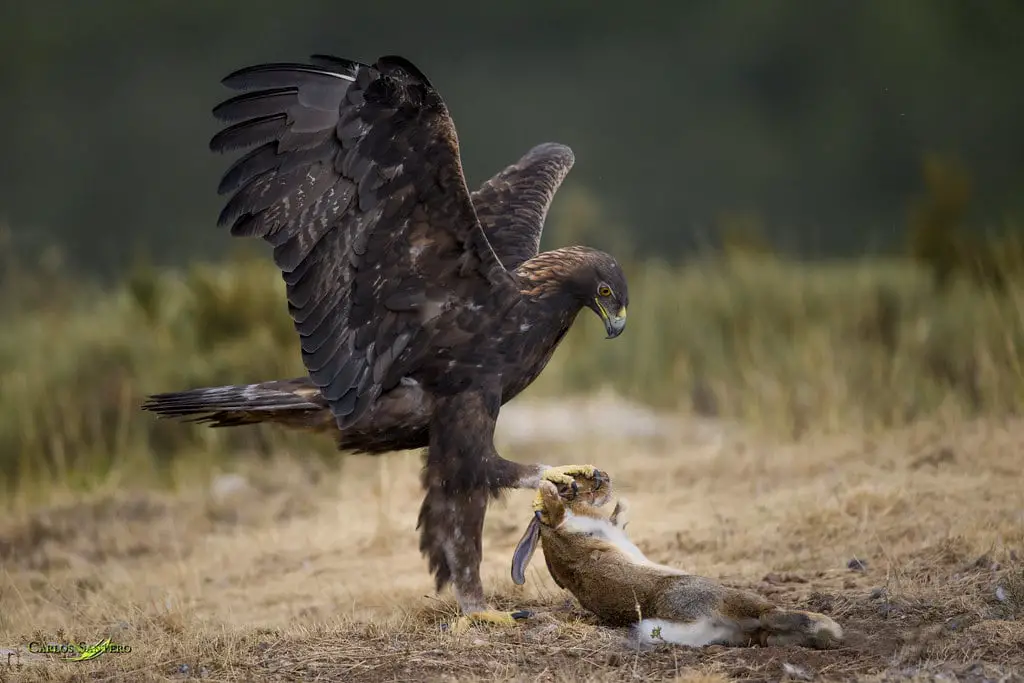

Golden Eagle and Rabbit
Defensive adaptations
- Defensive mechanism: Rabbits are agile animals kicking their hind legs and running quickly to escape from predators. They show zig zag jumping to dazzle the predator. Rabbits loudly thump their back feet to alert other rabbits from threats except for volcano rabbits (Romerolagus diazi) give a variety of calls.
- Camouflage: Rabbits and hares can easily blend with their surroundings with the help of their natural cream, brown, and buff fur. Arctic rabbits are white to camouflage in snow but their fur turns reddish brown in the fall season. Young rabbits freeze themselves to avoid predators because camouflage works when you’re motionless.
Behavioral Adaptations
Foraging behavior: Foraging in rabbits includes grazing grass, browsing leaves, and digging up roots to chew but they have an adaptation to change their nutrition according to seasonal changes. Rabbits are both active at dawn and dusk but mostly nocturnal and eat their poops during the relaxation season.
Social behavior: Rabbits are referred to as most social creatures mostly living together during breeding season and occasionally for foraging purposes in small groups.
Territorial behavior: Rabbits mark their territory ownership by releasing pheromones through scent glands around a specific place. This territorial behavior is mostly for breeding and reproduction.
Binky: Binkying of a rabbit is a large jump or a twisting leap in midair. Rabbits show binky behavior when they are happy and full of energy. It’s delightful to watch these fluffs binkying.
Defensive mechanism: Rabbits are agile animals kicking their hind legs and running quickly to escape from predators. They show zig zag jumping to dazzle the predator. Rabbits loudly thump their back feet to alert other rabbits from threats except for volcano rabbits (Romerolagus diazi) give a variety of calls.
Reproduction
Female rabbit is called a doe. Male rabbit is called a buck. Newborn rabbits are called kits. Rabbits are able to breed at an average of six months. Doe can conceive at any time in the year during her lifetime. Doe shows receptive behavior by hopping and flattening on the floor.
After mating, Doe kicks away the buck. Copulation lasts for 30 to 40 seconds. The gestation period is short, ranging from 29 to 36 days with an average of 31 days. Doe produces a litter containing one to twelve kits. Every year, a doe kindles eight litters.
Female rabbits usually kindle at dawn. After kindling, kits are naked and shut-eyed. They opened their eyes after one week. The female makes fake burrows for rearing her young. Rabbit milk is full of nutrients, enough for kittens one time a day. Just after 1 week of giving birth, she is again ready to conceive.
Mortality rate of juvenile rabbits is high. That’s why nature makes their reproduction rate much higher to balance this condition.

Economic Importance
Rabbits are of economic importance for people whether it is wild or domestic. Among hunters, it is important for sport, food, and fur. Rabbit meat as a high source of meat with delicate flavor is popular among many cultures. Domestic rabbits are kept as livestock to produce high-protein meat.
Every year, approximately 1.2 billion rabbits are slaughtered to meet the meat demand worldwide. Rabbit meat is popular in China, the United Kingdom, Europe, France and Spain. In addition, rabbits are used for milk and pelts. Rabbit’s milk is the richest among all mammal’s milk.
Diseases and Cure
Common diseases of rabbits are dental problems, gastrointestinal infections (GI stasis) , uterine problems, foot sores and parasites. Myxomatosis is a disease found in all domesticated rabbits caused by a myxoma poxvirus. Dental and digestive problems lead to mortality in young rabbits.
Treatment: In nature, adult rabbits cure themselves on their own while pet rabbits require proper medical treatment by an able veterinary doctor because they don’t have a natural habitat to recover. Vaccines are introduced to protect rabbits from diseases.
Conservation Status
According to the International Union of Conservation of Nature (IUCN), half of the world’s rabbit species are in danger of extinction. Their population size is highly declining due to human consumption and environmental changes.
The Japanese rabbit species Amami and the common European rabbits are listed under endangered species. cuniculus is endangered mostly in Spain, France, and Portugal. However, the most common American rabbits, Cottontails, do not appear in the Near Threatened (NT) list.
Literature and Cultural Value
Rabbits are referred to as innocent characters by folks easily connected to all kinds of youth. To portray trickery and sharp thinking, there are rabbit characters in stories such as Peter Rabbit and white rabbit. In Richard Adams’s “Watership Down”, Rabbits are themed for survival, leadership, and community.
Adorable creatures of God, Rabbits are positioned as a symbol of spring and fertility in various folks and cultures.
- In Christianity, Buddhism, and Judaism “The Three Rabbits motif” represents the renewal of life and several other positive meanings. It’s the subject of curiosity as the precise meaning of this three-rabbit motif is unclear.
- In the Chinese New Year, the Rabbit is one of the twelve celestial animals in the Chinese Zodiac.
- In Japanese culture, it is common to say that rabbits live on the moon and make their favorite sticky rice dish mochi.
- In Jewish culture, rabbits are a symbol of cowardice.
Do you remember the trickster Bugs Bunny and Br’er Rabbit?
FAQs- Frequently Asked Questions
1- What are rabbits known for?
There are many things that rabbits are known for such as fast reproduction, social behavior, coprophagy, activeness at both dawn and dusk, and their long ears which keep them alert of threats.
2- What are 5 facts about rabbits?
- Rabbits have the unique power of swimming.
- They are known for their fast speed
- Their eyes are turning around 360 degrees
- Rabbits can’t vomit
- Rabbits make good pets
- They live between 10 and 13 years
- They sleep 8-9 hrs a day.
3- What are the 7 characteristics of rabbits?
- Rabbits use secret codes to communicate with their partner.
- They have 2 pairs of ever-growing incisors
- Rabbits have long ears that rotate around 180 degrees and detect the exact location of sound.
- They have very fast speeds as they jump between 3 to 4 feet high and 9 ft horizontally.
- They are very self-groomed and clean like cats.
- Rabbits are happy in the company of their own species.
- They show binky when they feel happy and energetic.
4- What is a female rabbit called?
A female rabbit is called a doe.
5- What do rabbits eat?
Rabbits preferred to eat hay, grass, soft green vegetables, fruits, and munching carrots.
6- Where do rabbits live?
Rabbits live in various habitats like forests, grasslands, wetlands, deserts, woods, and meadows. They live underground except for cottontails.
7- What is a pregnant rabbit called?
Pregnant rabbit is also called a doe however when a doe’s giving birth, it’s called kindling.
Learn More About Rabbits
On this page, you are invited to browse our articles about some of the fascinating ways that rabbits behave.
These articles answer common questions about rabbits, including what they eat, when they’re most active, their reproductive cycle and process, and how they interact with humans in various environments.
Scroll down to learn more about some of the unique things that rabbits do and discover why they act the way they do.

Tan Rabbit
Introduction When it comes to rabbits, the Tan Rabbit stands out due to its unique characteristics and charming appearance. This

The Best Habitat for Pet Rabbits
Creating an Ideal Indoor Habitat for Pet Rabbits Establishing the **best habitat for pet rabbits** primarily involves replicating their natural

The History and Origin of Domesticated Rabbits
The Fascinating History of Domesticated Rabbits Domesticated rabbits have a long and captivating history that dates back to ancient times.

The Impact of Diet on Rabbit Health
The Importance of a Balanced Diet for Rabbit Health A healthy diet plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall

The Importance of Socialization for Rabbits
Why Socialization is Crucial for Rabbit Health Rabbits are naturally social animals that thrive on interaction with their environment and

The Lifespan of Different Rabbit Breeds
Introduction to Rabbit Lifespan The lifespan of a rabbit can vary significantly based on several factors including breed, diet, and

The Nutritional Needs of Pet Rabbits
The Nutritional Needs of Pet Rabbits When it comes to caring for your pet rabbit, understanding their nutritional needs is

Thrianta Rabbit
Introduction to Thrianta Rabbit **The Thrianta Rabbit is a stunning and friendly rabbit breed known for its striking red fur

Understanding Rabbit Behavior and Communication
Introduction to Rabbit Behavior and Communication Understanding rabbit behavior and communication can be both fascinating and essential for anyone who

Velveteen Lop
Introduction to the Velveteen Lop Rabbit The Velveteen Lop is one of the most adorable and beloved rabbit breeds that

Vienna Blue Rabbit
What is Vienna Blue? Vienna Blue is a specific breed of domestic rabbit known for its striking blue-grey fur and

Vienna Rabbit
Introduction to the Vienna Rabbit The Vienna Rabbit is a captivating breed, renowned for its unique characteristics and charming appearance.

Vienna White Rabbit
What is Vienna White? Vienna White is a type of white paint known for its high opacity and pure white

What Are Baby Rabbits Called?
What Are Baby Rabbits Called? Baby rabbits are called “kits” or “kittens”. This term is used universally regardless of the

What Do Rabbits Eat?
Understanding Rabbit Diets The first thing you need to know about rabbits is that their dietary needs are quite specific

What Do Rabbits Symbolize?
What Do Rabbits Symbolize in Different Cultures? Rabbits have fascinated humans for centuries and carry different symbolic meanings across various

What Do Wild Rabbits Eat?
Introduction to Wild Rabbits’ Diet If you’re curious about what wild rabbits eat, you’re in the right place. Wild rabbits

What Eats Rabbits?
What Eats Rabbits? Rabbits are a common target for various predators in the animal kingdom. Understanding which animals eat rabbits

What Fruits Can Rabbits Eat?
What Fruits Are Safe for Rabbits? If you’re a rabbit owner, you might be wondering what fruits are safe for

What Is a Group of Rabbits Called?
What Is a Group of Rabbits Called? A group of rabbits is commonly called a herd, colony, nest, or warren.

What to Feed Baby Rabbits Without a Mother
Introduction Feeding a baby rabbit without a mother can be a challenging and delicate task. Baby rabbits, or kits, require
