HYENAS
Hyenas are one of the longest-living carnivores known for their proficient hunting. They are the most well-known and destructive complex creatures. Due to their aggressiveness, they are popular among predators. Above all, they are smart, socially intelligent, and more curious than others.
Scientific Classification
|
Kingdom |
Animalia |
|
Phylum |
Chordata |
|
Class |
Mammalia |
|
Order |
Carnivora |
|
Suborder |
Feliformia |
|
Family |
Hyaenidae |

Species
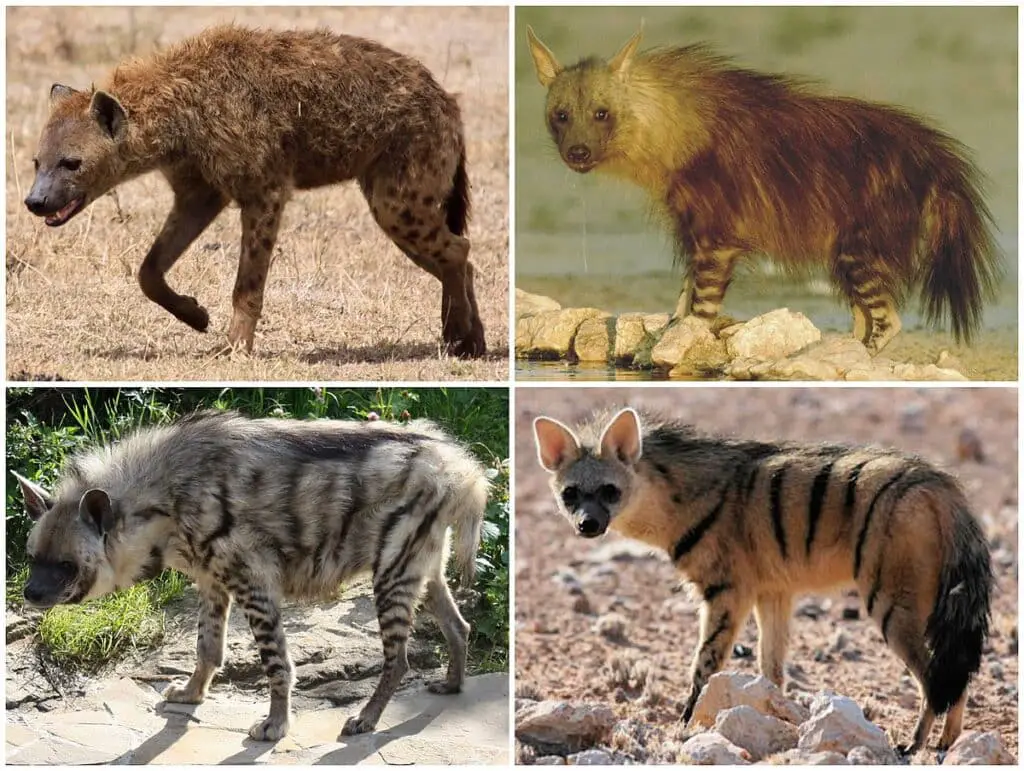
Among 4 different genera, hyenas have only four extant species. Hyenas have their own unique family. They are the closest relatives of mongooses and civets.
|
Names |
Description |
|
Spotted hyena (Crocuta crocuta) |
These are apex predators. The spotted hyena is one of the largest species with a unique body structure.
|
|
Striped hyena (Hyaena hyaena ) |
These hyenas have a dog-like appearance and black stripes lie on grayish bodies.
|
|
Aardwolf (Proteles cristatus) |
It is not a wolf but a rare species of hyena. Aardwolf is yellowish brown in color and has black stripes on his coat. Their populations are abundant.
|
|
Brown hyena (Parahyaena brunnea) |
This is the smallest member of the hyena family and has a short tail with a dark brown coat.
|

Physical Characteristics
Size: Female hyenas are larger than males. Females are 84 to 89 cm long rather than males. Males are 79 to 86 cm long.
Weight: On average, males weigh between 56 to 63 kilograms. In contrast, females may vary between 67 to 75 kilograms.
Speed: Hyenas are fast runners. They chase down prey at the speed of 37 miles per hour.
Body: Hyenas have a large head and muscular body. All of its body parts, including ears, stomach, jaws, and muscles, are very strong. Thay have long forelegs and powerful necks.
Dentition: They have 28 to 34 teeth. 6 to 7mm long canines and 4mm long incisors. Their teeth are as sharp as blades. Sharpness helps them in the grinding of bones.
Tail: Hyena’s tails are short and bushy. Their tail is dark and gets black at the tip.
Coat colouration: Their coat is short and ranges in color from yellow to grey, and brown to black, with dark brown spots and black stripes. Other hyenas have fluffy and reddish fur.
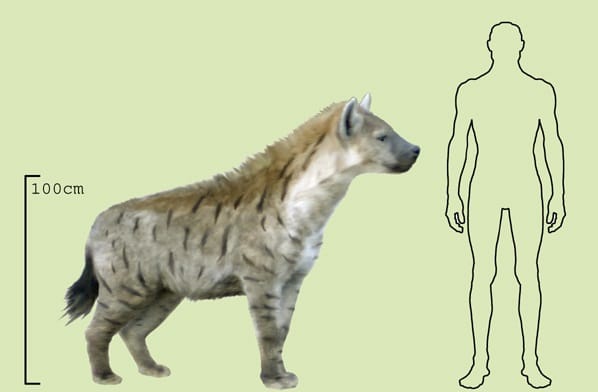
Hyenas Size and Weight
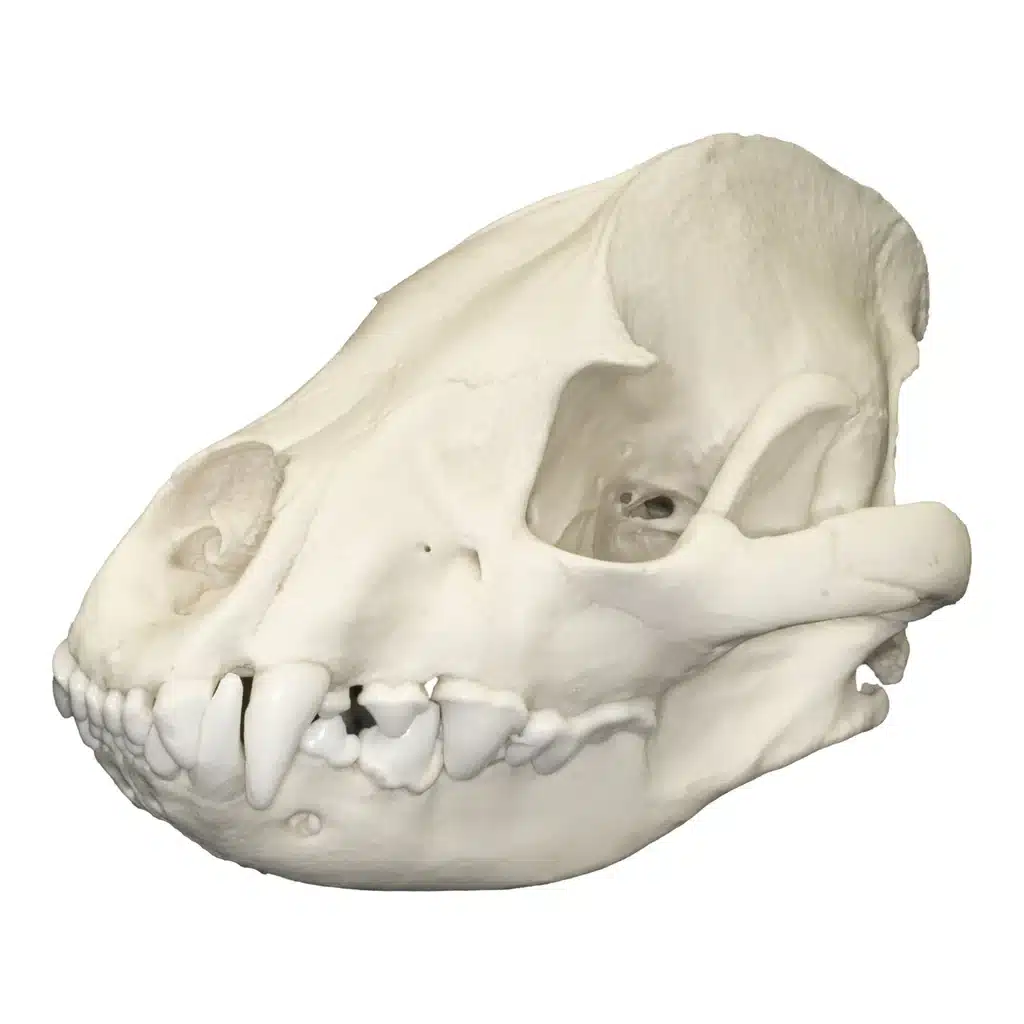
Hyenas Skull

Hyenas Speed
Distribution and Habitat
A large number of hyenas, including all species, are found in Sub-Saharan Africa. Geographically, they are divided in different regions of Africa and also in the Sub-continent. Almost 80 percent of their population lives in the African countries of Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
Masters of savanna tend to live in grasslands, woodlands, deserts and mountainous regions. Brown hyenas inhabit scrublands. At the same time, aardwolf prefers to live in dry open savannas.
They occupy a number of habitats, from savannas to deserts. In that way, they maintain their habitat well. They sleep in pools, holes, and bushes.
Diet and Digestion
Hyenas are skilled mammals lying under order Carnivora. They generally feed on gazelles, zebras, and wildebeest. All of their species are bone-cracking. Their jaws and teeth are stronger than other mammals which exert a full force in grinding of bones. Aardwolf has a different diet than others. They use their tongues to lick up termites.
Hyenas are opportunistic in diet. Their stomachs allow them to consume and digest the carcasses of other animals. They can digest everything except hooves, nails, and horns. The parts of prey that are not digested are defecated in the form of hard pellets. Aardwolf diet helps them in the digestion of cellulose.
Behavioral Adaptations
Hunting
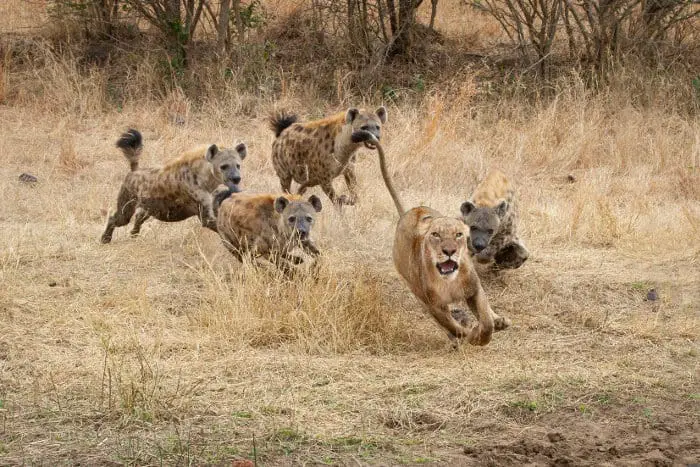
Hyenas are known as scavengers, but in reality, they hunt 70 percent of the food on their own. As tireless trotters, they cover a long distance to catch prey. They are capable of chasing down large prey. They hunt in groups that can increase their chance of hunting.
Spotted hyenas are successful hunters among big cats that prey on wildebeest, gazelles, zebras and antelopes. Brown and striped hyenas are scavengers and eat carrion. Hyenas are nocturnal and can travel up to 80 km at night for hunting.
Social Behavior
Hyenas are cunning in nature. They are socially active and live in large communities called “Clans.” Their clan consists of 80 individuals, including males, females, and their offspring. To maintain clans is a complex process. Females are more dominant and aggressive than males.
Hyenas have a matriarchal society. The alpha female is the leader of a clan, which helps them maintain their structure and bonds. Hyenas structures are well organized. Individuals of clans cooperate in the hunting of large prey. Their communities help them to survive.
Camouflage
Camouflage is a tactic that organisms use to blend itself with their surroundings. Hyenas are brown, golden or gray in color and have bushy manes with black stripes on their back. They easily camouflage themselves in rocks, dark places or among trees. They silently wait for prey and swiftly attack them.
Communication
Vocalization:
Hyenas are skilled hunters. They have the ability to vocalize through which they communicate with other members of the community or rivals. Hyenas use different sounds, including yells, grunts, howls, and whoops. Their laughter is similar to human laughter.
Scent marking:
Their anal glands secrete a substance called “Paste.” They rub their anus on bushes to show their dominance. Urine marking is a dominant method that they use to communicate, warn others, and protect themselves. Their scent lasts for a long time.
Reproduction and Parenting
Hyenas have a distinctive reproductive system among mammals. Males become sexually mature at 3 to 4, while females conceive at 2 to 5 years. Their gestation period is around 110 days. Female sexual organs are externally similar to men. Female spotted hyenas have psuedopenis, which makes them different from men. They control who mates with them.
They give birth to two cubs at a time in isolated areas. Their cubs started to fight for food or more milk. Cubs feed milk continuously for 14 days. After some days, they went to other dens which aardvarks previously dug. Hyenas raise their cubs.
Young males leave the clan at the age of three but female cubs stay with their mothers in the clan.Young males move to other clans for breeding.
Mortality rate and Lifespan
The mortality rate among hyenas is high. Hyenas mortality depends on their environmental conditions. The first six months are critical for cubs. But their mortality rate remains moderate when they are at 2. They are at the risk of their lives when they become adults.
In the wild, they can live around 12 years. Some individuals can live longer. They live up to 20 to 25 years in the wild and 40 years in captivity.
Ecological Importance
As a natural predator as well as scavengers, hyenas eat up carcasses. Hyenas play a pivotal role in the ecosystem and cooperate to keep the forest free from overgrazing. They clean up the wastes from landscapes which helps to keep the ecosystem clean.
Their crushing of bones prevents us from widespread infections like anthrax. They work as a game changer for the ecosystem.
Conservation status and Efforts
Hyenas’ population is listed as least concerned on the IUCN Red List. According to the current report of the International Union for Conservation of Nature(IUCN), hyenas are widespread in Africa, and they range between 27,000 and 47,000. Their population decreased due to deforestation and illegal hunting. They are suffering from human wildlife conflict.
We secure their species by giving them a pure and fearless habitat, providing food and protection. It is necessary to educate people about the significance of hyenas, how they keep our environment safe, and why they overgraze.
Hyn Fun Facts
- Females are aggressive and dominant over males.
- Hyenas produce 11 different sounds.
- They are important to study the evolution of carnivores.
- Their jaws exert 1100 pounds square per inch of force.
- Out of all, they are tireless trotters that cover a long distance without getting tired.
- Spotted hyenas are also known as “laughing hyenas.”
- Hyena is primarily a hunter, not a scavenger.
Cultural Value
- In numerous cultures, hyenas symbolize both positive and negative creatures.
- The Masai people of Tanzania respect hyenas due to their survival skills.
- According to the Doctrine of Ethiopian Orthodox, Hyenas are unclean animals that represent sexual deviancy and lawlessness.
- In some African tribes, hyenas symbolize royalty and power, associated with ancestral phantoms.
- In mythology, hyenas are often associated with supernatural powers and darkness.
- In a Hollywood movie, “The Lion King, hyenas are portrayed as evil.
FAQs- Frequently Asked Questions
Q- Are hyenas related to dogs or cats?
Hyenas are more closely related to cats than dogs, though they belong to their own unique family, Hyaenidae.
Q- What do hyenas eat?
Hyenas are primarily scavengers but also hunt, feeding on a variety of animals, including carrion, small mammals, and even large prey like wildebeest.
Q- Why do hyenas laugh?
The “laughter” of hyenas is a form of communication, often signaling social status, excitement, or anxiety within the group.
Q- Do hyenas live in packs?
Yes, hyenas live in social groups called clans, which are led by a dominant female and can consist of up to 80 members.
Q- Are hyenas dangerous to humans?
While hyenas generally avoid humans, they can be dangerous if they feel threatened or if food is scarce.
Q- How long do hyenas live?
Hyenas typically live around 12 years in the wild but can live up to 25 years in captivity.
Q- Why do hyenas have such strong jaws?
Hyenas have powerful jaws to crush bones, which allows them to access nutritious marrow and consume nearly all parts of their prey.
Q- Do hyenas hunt alone or in groups?
Hyenas often hunt in groups, especially when targeting large prey, though they can also hunt alone for smaller animals.
Q- Are hyenas nocturnal?
Yes, hyenas are primarily nocturnal, hunting and scavenging during the night.
Q- How do hyenas interact with other predators?
Hyenas are both competitors and scavengers, often clashing with lions, leopards, and wild dogs over food.
Q- What are 5 interesting facts about hyenas?
Hyenas have a matriarchal society, can crush bones with their jaws, are excellent hunters, produce a variety of vocalizations, and have a digestive system that can process almost all parts of their prey.
Q- Why are hyenas famous?
Hyenas are famous for their “laughing” vocalizations, their role as both scavengers and hunters, and their strong social structures.
Q- What are a few lines about hyenas?
Hyenas are intelligent, social animals known for their unique vocalizations and powerful jaws. They live in clans and play a crucial role in maintaining the balance in their ecosystems.
Q- Where do hyenas live?
Hyenas primarily live in Africa, inhabiting savannas, grasslands, woodlands, and even mountainous regions.
Q- What makes a hyena special?
Hyenas are special due to their strong social bonds, matriarchal clan structures, and the ability to digest bones and other tough materials.
Q- What is unique about the hyena?
Hyenas are unique for their matriarchal societies, with females being larger and more dominant than males, and their incredible bone-crushing jaws.
Q- What is the role of a hyena?
Hyenas play the role of both predator and scavenger, helping control prey populations and clean up carrion in their habitats.
Q- How do hyenas help humans?
Hyenas help humans by controlling populations of pests and cleaning up animal remains, which can reduce the spread of disease.
Q- Is a hyena friendly?
Hyenas are not typically friendly to humans and can be dangerous if approached, especially in the wild.
Q- What are hyenas’ abilities?
Hyenas have strong jaws capable of crushing bones, high stamina for long-distance running, and a complex social structure.
Q- What is the behavior of a hyena?
Hyenas are social, territorial, and often nocturnal, engaging in complex communication within their clans and exhibiting both cooperative hunting and scavenging behaviors.
Learn More About Hyenas
On this page, you are invited to explore our articles about the fascinating behaviors of hyenas.
These articles answer common questions about hyenas, including their diet, activity patterns, social structures, reproduction, and interactions with their environment and other species.
Scroll down to discover the unique traits of hyenas and gain insights into why they behave the way they do.

How big is a hyenas poop?
“`html How Big Is a Hyena’s Poop? A hyena’s poop typically measures about 1 to 1.5 inches (2.5 to 3.8 cm) in diameter and can reach lengths of 3 to 6 inches (7.6 to 15

Why Do Hyenas Laugh?
“`html Hyenas laugh—and it’s not because they heard a good joke. Their iconic giggles are a clever communication tool, used to express emotions, establish pecking orders, and even plan group activities. Let’s dive deep into

Can You Have a Hyena as a Pet?
No, you generally cannot have a hyena as a pet. It’s illegal in most places, highly unsafe, and raises serious ethical concerns. Let’s dive into why your dream of a pet hyena should probably stay

How Do Hyenas Give Birth?
Understanding the Unique Birthing Process of Hyenas Alright, gather around, folks—because we’re diving into one of nature’s most peculiar birthing stories. Hyenas, specifically the spotted kind, have a jaw-droppingly unique way of welcoming their little

How Fast Can a Hyena Run?
“`html How Fast Can a Hyena Run? Alright, let’s talk about one of nature’s most misunderstood speedsters: the hyena. Sure, they get a bad rap in pop culture, but these creatures are far more fascinating

How Strong Is a Hyena’s Bite?
“`html Understanding the Hyena’s Incredible Bite Strength Alright, let’s get straight to it – hyenas boast one of the strongest jaws in the animal kingdom, hands down. If you’ve ever wondered just how powerful their

What Is a Hyena?
“`html Understanding Hyenas: An Introduction Alright folks, let’s talk about the most misunderstood joke-tellers of the animal kingdom—hyenas! These fascinating creatures, often caricatured as sneaky scavengers, are so much more than their bad PR suggests.

What Kind of Animal Is a Hyena?
“`html Hyenas are carnivorous mammals from the family Hyaenidae, known for their quirky quirks, bone-crushing bites, and downright fascinating lifestyles. These misunderstood wildlife wonders bring a lot more to the table than their haunting “laughs”—so

What Do Hyenas Eat?
“`html The Diet of Hyenas: What Do They Eat? Hyenas are nature’s ultimate clean-up crew, but there’s way more to their dining habits than just “scavenger chic.” These quirky carnivores are expert hunters, bone crushers,

Can You Legally Own a Hyena in the U.S.?
“`html So, you’re thinking about owning a hyena, huh? Whether it’s their iconic laugh or their downright intimidating presence, hyenas are fascinating creatures, no doubt. But before we dive into this wild adventure, there’s something

What Is a Baby Hyena Called?
“`html A baby hyena is called a cub. Unveiling the Early Life of Hyena Cubs Meet the baby hyena, nature’s tough little cub ready to steal the spotlight! These cubs are more than just adorable—they’re

How Big Can a Hyena Get?
“`html Understanding Hyena Sizes: The Big, Bold World of Hyenas Spotted hyenas, the biggest and baddest of the hyena family, can stretch up to 6 feet (1.8 meters) long, stand about 3 feet (0.9 meters)

What Does a Hyena Sound Like?
“`html Hyenas aren’t just the comedians of the animal kingdom; their vocal talents are a masterclass in wildlife communication. From their iconic “laughter” to haunting nighttime whoops, these fascinating creatures have a lot to say—and

Is a Hyena a Dog or Something Else?
“`html Alright, let’s crack this open—no, a hyena is NOT a dog. It’s also not a cat. It’s just… well, it’s a hyena: wild, fascinating, and utterly its own thing. Hyenas belong to a family

What Eats a Hyena in the Wild?
“`html Who Preys on Hyenas in the Wild? Lions, leopards, crocodiles, and, of course, humans play the role of predators when it comes to hyenas. At first glance, hyenas might seem untouchable—tough, scrappy, and always
